Table of Contents
What GAO Discovered
Medicare sets caps on equally of its types of health practitioner graduate health-related training (GME) payments (immediate and indirect) to instructing hospitals. Caps on these payments identify the variety of doctor trainees—known as residents—that each and every payment form supports. Hospitals can use other resources of resources to prepare additional citizens than these caps. Medicare information display that in 2018, 70 per cent of hospitals were more than a single or both equally caps on Medicare-funded inhabitants, and 20 % of hospitals have been under one particular or both equally caps. For both equally payment sorts, hospitals funded drastically additional slots about the cap than they remaining unfilled, but Medicare nevertheless funded the large the greater part of resident slots.
Graduate Medical Education and learning (GME) Residents and Slots by Medicare Payment Variety and Funding, 2018
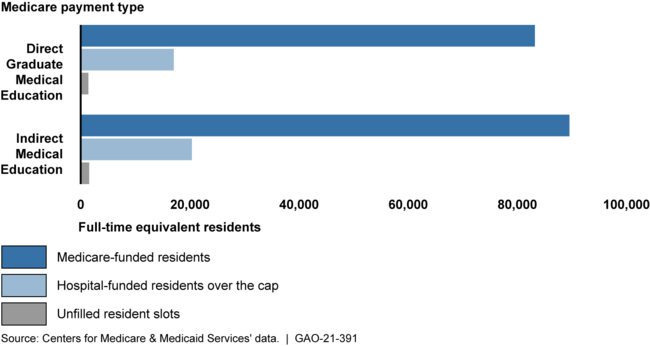
Notes: Medicare’s payments for GME are dependent, in component, on the range of full-time equal citizens that a medical center trains. Caps reflect the variety of residents suitable for the two GME payment styles. Direct Graduate Health care Education payments offset immediate prices of GME coaching, these as resident salaries, and Indirect Medical Education and learning payments offset oblique expenses of GME training, this kind of as the additional expense of resident supervision.
Medicare offers hospitals starting up their first new GME courses 5 decades to set up and increase their GME plans before their caps are set. After established, hospitals’ resident caps are generally everlasting. GAO questioned GME stakeholders about current proposals to extend this window further than 5 a long time. Stakeholders mentioned that extending this time window could consequence in much larger caps and a lot more citizens education at some hospitals since the hospitals would have additional time to, for instance, recruit extra college and people or commence packages in more advanced specialties just before caps are established. Some stakeholders representing companies and a researcher recommended targeting the extension to less than-resourced hospitals—such as individuals found in rural spots or areas with overall health care service provider shortages—which often experience challenges in rapidly recruiting faculty and ensuring a wide variety of academic activities for residents. On the other hand, they famous that extending the cap-institution window would not handle all problems that below-resourced hospitals face when setting up new GME applications.
Why GAO Did This Review
Scientific tests have proven the United States faces a scarcity of medical professionals, building it progressively tricky for persons to accessibility desired well being treatment. Medical professionals will need GME education in advance of they can observe medication independently and usually follow in the same geographic spot as their coaching.
The wide bulk of federal funding for this training—about $15 billion in 2018—supports medical doctor coaching by way of the Section of Overall health and Human Services’ Medicare GME payments. Medicare offers payments to educating hospitals to offset charges of training whole-time equal residents, up to a capped quantity of resident slots for every clinic. For most hospitals, caps mirror the selection of people that Medicare funded in 1996 for hospitals setting up their very first new GME system in 1997 or later, caps were being centered on the variety of Medicare-funded citizens qualified at the finish of a particular time window.
GAO was requested to critique Medicare GME funding. This report, amid other challenges, describes the extent to which hospitals had been about or under their Medicare GME caps and stakeholders’ views on extending the time window ahead of new caps are founded. GAO analyzed 2018 Medicare facts (the most modern out there at the time of GAO’s assessment), reviewed agency documentation, and interviewed eight selected stakeholder groups—including a GME accreditor and groups symbolizing wellbeing treatment providers—identified via previous GAO perform.
The Office of Well being and Human Companies furnished specialized feedback on a draft of this report, which GAO integrated as appropriate.
For much more data, speak to Michelle Rosenberg at (202) 512-7114 or rosenbergm@gao.gov.












