Table of Contents
Researchers in the Uk and Spain have applied a novel drug screening technique to recognize compounds that could provide as efficient antivirals against serious acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) – the agent that leads to coronavirus sickness 2019 (COVID-19).
The workforce employed a quantum-influenced gadget in combination with a a lot more standard fingerprinting technique to research for drugs that are comparable to remdesivir, the only antiviral towards SARS-CoV-2 that is presently permitted for human use.

“The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated the want to establish new therapeutics at speed, such as through drug repurposing,” claims the team from Fujitsu Technological innovation Options in Madrid and King’s University Healthcare facility in London.

When both equally designs predicted the antiviral drug GS-6620 as the best compound, the quantum-dependent model predicted the antiviral BMS-986094 as next greatest. Both of these compounds have been at first created to take care of the hepatitis C virus.
The far more common Tanimoto model also predicted distinctive forms of vitamin B12 as prospective antiviral candidates.
In vitro analyses discovered that BMS-986094 and the diverse sorts of B12 were productive at inhibiting the replication of SARS-CoV-2 variants.

“While BMS-986094 can lead to secondary consequences in people as founded by phase II trials, these results counsel that vitamin B12 warrants thing to consider as a SARS-CoV-2 antiviral, specifically given its extended use and deficiency of toxicity in individuals, and its availability and affordability,” writes Rocio Martinez-Nunez and colleagues.


“Our facts illustrate the energy of using quantum-encouraged computing for drug repurposing,” they incorporate.

A pre-print version of the analysis paper is available on the bioRxiv* server though the report undergoes peer assessment.
Treatments that can be promptly deployed are urgently required
Since the COVID-19 outbreak initially began in late December 2019, powerful investigate and enhancement efforts have led to the unexpected emergency use authorization and mass roll-out of quite a few helpful vaccines in opposition to SARS-CoV-2.

“However, the ongoing emergence of new variants, unique immunization costs, provide chain difficulties, as well as the presence of smaller or larger sized outbreaks underlie the prerequisite for urgent solutions that can be fast deployed,” claims Martinez-Nunez and colleagues.

Drug repurposing refers to the method by which accredited medications are used to treat a disorder they had been not initially developed to treat.
Virtual screening has become vital in the early levels of drug discovery, but the process is normally time-consuming since it frequently relies on measuring chemical similarities among molecules.
Accordingly, most very well-recognized methods use 2D molecular fingerprints to consist of structural info about molecules. Having said that, these techniques do not take into account features of molecular structures this kind of as 3D folding.
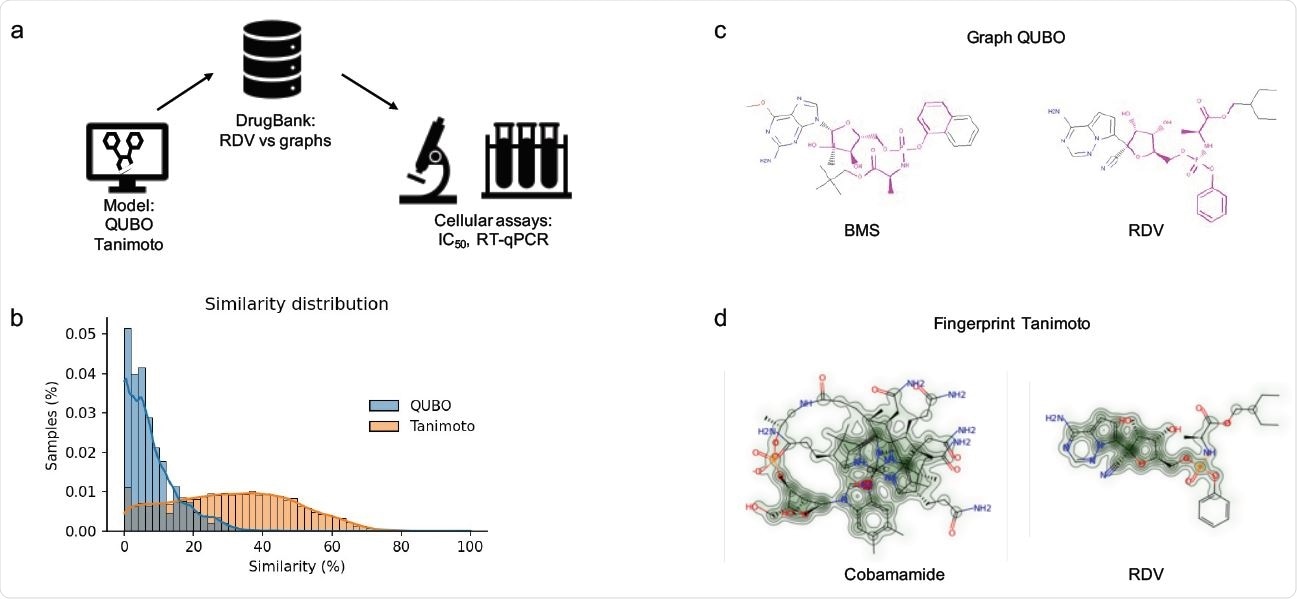
Molecular modeling. (a) pipeline used in our venture. RDV was initial modeled as a graph and then screened versus the DrugBank dataset. (b) Comparison of samples from the DrugBank predicted as similar to RDV by QUBO (blue) and Tanimoto (orange) types. (c) Graphic representation of BMS-986094 (BMS, left) and RDV (correct) similarity in accordance to QUBO. The magenta shade signifies the very similar features between the two molecules, together with atoms as very well as bonds, though the relaxation of the representation is the non-very similar features. d: Graphic illustration of similarity for cobamamide (remaining) and RDV (ideal) generated by RDkit. The escalating green colour signifies a lot more similarity concerning molecules.
Where by does quantum-encouraged computing come in?
The 3D information received from a provided molecule can be encoded as a graph, say Martinez-Nunez and colleagues.

“In buy to estimate the similarity in between molecules, a new graph that has information and facts with regards to the two molecules is essential, permitting for much better and speedier comparisons to clear up an optimization trouble recognised as the Highest Unbiased Established (MIS) that extracts the related pieces of those two graphs,” describes the crew.

By utilizing quantum-inspired computing, mathematical styles are ready to control this form of information while shortening execution instances by up to 60-fold.
The problem with remdesivir
Remdesivir is now the only antiviral drug authorised for use in opposition to SARS-CoV-2, although yet another compound termed molnupiravir is also emerging as a possible prospect.
Nonetheless, both of these compounds are associated with various facet effects, such as nausea and hepatic impairment. They are also expensive and as a result unaffordable in several nations and settings.

“There is, consequently, an urgent will need to establish novel antiviral compounds that exhibit low to no facet consequences and that are easily and economically accessible,” generate the researchers.

What did the scientists do?
The researchers utilized a Quadratic Unbounded Binary Optimization (QUBO) design that operates on a quantum-influenced machine to research for compounds identical to remdesivir.
They modeled remdesivir as a graph and then screened the DrugBank databases for compounds presently authorized for human use. The best parameters in the algorithm had been founded, and the MIS issue was solved within just the conflict graph produced.
The team also employed a a lot more conventional fingerprint process – the Tanimoto index – that runs on a standard notebook.
What did the study discover?
Both solutions predicted quite a few compounds that exhibited similarity to remdesivir, with GS-6620 predicted as the leading compound by both equally designs. The QUBO product predicted BMS-986094 as the second-most effective candidate and Tanimoto predicted a number of forms of cobamamide, also regarded as vitamin B12.
Up coming, the staff done cultured cell assays to decide the SARS-CoV-2 inhibitory capabilities of the compounds. This exposed that BMS-986094, cobamamide, hydroxocobalamin, and methylcobalamin all proved successful at concentrations lying within ranges ideal for human use.
Lastly, the scientists showed that these compounds were productive at inhibiting the replication of a variety of SARS-CoV-2 variants, together with B.1.1.7 (also named Alpha), B.1.351 (Beta), and B.1.617.2 (Delta).
What did the authors conclude?
Martinez-Nunez and colleagues say the knowledge disclosed novel compounds that could inhibit SARS-CoV-2 replication, based on the QUBO design and the much more conventional Tanimoto fingerprint.

“BMS warrants additional investigation, although vitamin B12 is quickly available from several resources. It is inexpensive, can be self-administered by patients, is readily available throughout the world, and shows minimal-to-no toxicity at higher doses,” they create.


“Our screening strategy can be utilized in upcoming searches for novel pharmacologic inhibitors, hence supplying an tactic for accelerating drug deployment,” concludes the crew.

*Essential Discover
bioRxiv publishes preliminary scientific stories that are not peer-reviewed and, hence, should not be regarded as conclusive, tutorial scientific practice/wellbeing-relevant actions, or handled as founded data.